CSS容器的包含块
in Origin Pageviews
一个元素的尺寸和位置经常受到包含块的影响,大多数情况下,包含块就是这个元素的祖先块元素的内容区,但并不总是这样。
当一个客户端代理如浏览器展示一个文档时,对于每一个元素,他都产生了一个盒模型。每一个盒子都被化成了四个区域:
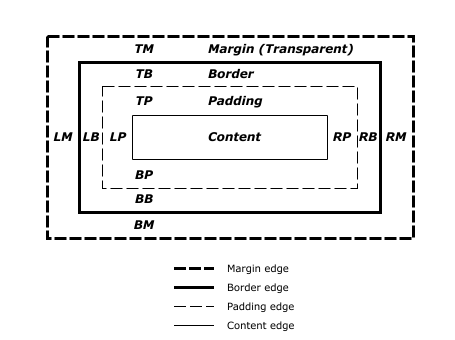
元素的尺寸及位置,常常会受到它的包含块的影响。对于一些属性,例如width,height,padding,margin,绝对定位元素的偏移值(如position被设置成absolute或fixed,当对其赋予百分比值时,这些值的计算值就是通过元素的包含块计算得来的)
确定一个元素的包含块的过程完全依赖于这个元素的position属性:
如果
position属性为static或relative,包含块就是由它的最近的祖先块元素(如inline-block,block或list-item元素)或格式化上下文(如 table container,flex container,grid container or the block container itself)的内容边缘组成的.如果
position属性为absolute,包含块就是由它的最近的position值不为static(即是fixed,absolute,relative或sticky)的祖先元素的内边距的边缘组成.如果
position属性是fixed,包含块就是由当前的可视窗口viewport组成.如果
position属性是absolute或fixed,包含块也可以是由满足以下条件的最近父级元素的内边距的边缘组成:transform或perspective的属性值不是none;If the property has a value different than
none, a stacking context (层叠上下文)will be created. In that case, the object will act as a containing block for anyposition: fixedelements that it contains.—Form transform
transform或perspective的属性值是可变的(will-change);filter的属性值不是none或者是可变的(will-change)(仅仅在Firefox中有效)
如上所述,如果某些属性被赋予百分比的话,它的计算值是由这个元素的包含块决定的。这些属性包括盒模型属性和偏移属性。
- 要计算
height,top及bottom中的百分比值是通过包含块的height值。如果包含块的height值会根据它的内容变化,而且包含块的position属性的值被赋予relative或static,那么这种情况百分比值为0。 - 要计算
width,left,right,padding,margin这些属性由包含块的width属性的值来计算它的百分比。
Example:
对于html:
<div id="demo">
<section>
<p>This is a paragraph!</p>
</section>
</div>
<p>标签是静态定位时,它的包含块是离它最近的块祖先元素section。div { background: beige; } section { display: block; width: 400px; height: 160px; background: lightgray; } p { width: 50%; /* => 400px*.5 = 200px*/ height: 50%;/* => 160px*.5 = 80px*/ margin: 5%; /* => 400px*.05 = 20px*/ padding: 5%;/* => 400px*.05 = 20px*/ background: blue; }
<!DOCTYPE html>
This is a paragraph!
- 当
<p>标签包含块为<div>元素,此时<section>不再是一个块容器(inline内联),所以此时不会在此处形成块级格式化上下文。会在<div>处形式格式化上下文,代码如下:
div {
background:beige;
}
section {
dispaly: inline;
background: lightgray;
}
p {
width: 50%; /* => half of the div's width*/
height: 200px;/* => 固定高度*/
background: blue;
}
- 当
<section>的position被设置成absolute;此时<p>元素的包含块是<section>。<p>元素的padding的百分比值会受到其包含块的影响。但是,如果包含块的box-sizing被设置成border-box,就不会存在这个问题。
div {
background:beige;
}
section {
position: absolute;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
width: 400px;
height: 160px;
padding: 30px 20px;
background: lightgray;
}
p {
position: absolute;
width: 50%; /* => (400px+20px+20px)*.5 = 220px*/
height: 25%;/* => (160px+30px+30px)*.25 = 55px*/
margin: 5%; /* => (400px+20px+20px)*.05 = 22px*/
padding: 5%;/* => (400px+20px+20px)*.05 = 22px*/
background: blue;
}
- 当把
<p>元素的position设置为fixed,所以它的包含块就是初始包含块(在屏幕上就是viewport)。如此,p元素的尺寸大小会随着浏览器窗口的大小而变化。
body {
background:beige;
}
section {
width: 400px;
height: 480px;
margin: 30px;
padding: 15px;
background: lightgray;
}
p {
positin: fixed;
width: 50; /* == (50vw - (width of vertical scrollbar)) */
height: 50%;/* == (50vh - (height of horizontal scrollbar)) */
margin: 5%; /* == (5vw - (width of vertical scrollbar)) */
padding: 5%;/* == (5vw - (width of vertical scrollbar)) */
background: blue;
}
- 当把
<p>的position设置为absolute,它的包含块是<section>,因为此时距离它最近的一个transform值不为none的父元素;
body{
background: beige;
}
section {
transform: rotate(0deg);
width: 400px;
height: 160px;
background: lightgray;
}
p {
position: absolute;
left: 80px;
top: 30px;
width: 50%; /* == 200px */
height: 25%; /* == 40px */
margin: 5%; /* == 20px */
padding: 5%; /* == 20px */
background: cyan;
}